A data structure is a way of organizing data that considers not only the items stored, but also their relationship to each other. Advance knowledge about the relationship between data items allows designing of efficient algorithms for the manipulation of data.
The heterogeneous linked list contains different data types in its nodes and we need a link, pointer to connect them. It is not possible to use ordinary pointers for this. So we go for void pointer. Void pointer is capable of storing pointer to any type as it is a generic pointer type.
Two. One queue is used for actual storing of data and another for storing priorities.
Stack. Because of its LIFO (Last In First Out) property it remembers its ‘caller’ so knows whom to return when the function has to return. Recursion makes use of system stack for storing the return addresses of the function calls.
Every recursive function has its equivalent iterative (non-recursive) function. Even when such equivalent iterative procedures are written, explicit stack is to be used.
Polish and Reverse Polish notations.
Prefix Notation:
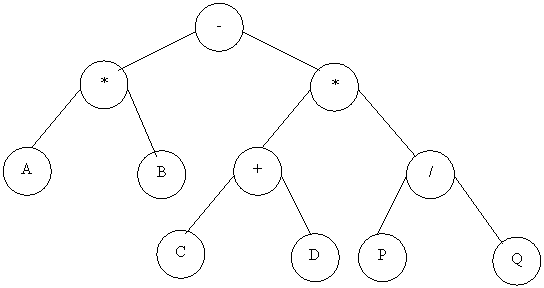
^ - * +ABC - DE + FG
Postfix Notation:
AB + C * DE - - FG + ^
(a) Insertion
(b) Selection
(c) Exchange
(d) Deletion
(d) Deletion.
Using insertion we can perform insertion sort, using selection we can perform selection sort, using exchange we can perform the bubble sort (and other similar sorting methods). But no sorting method can be done just using deletion.
21
Let us take a tree with 5 nodes (n=5)

It will have only 6 (ie,5+1) null branches. In general,
A binary tree with n nodes has exactly n+1 null nodes.
1014
For example, consider a tree with 3 nodes(n=3), it will have the maximum combination of 5 different (ie, 2 3 - 3 = 5) trees.
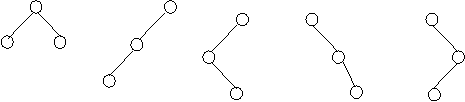
i ii iii iv v
In general:
If there are n nodes, there exist 2 n-n different trees.
(a) Array (b) Linked list (c) Stack (d) Queue (e) none
(b) Linked list
Backtracking
If the ‘pivotal value’ (or the ‘Height factor’) is greater than 1 or less than –1.
One. If there is only one entry possible in the bucket, when the collision occurs, there is no way to accommodate the colliding value. This results in the overlapping of values.
15.
In general:
There are 2 n-1 nodes in a full binary tree.
By the method of elimination:
Full binary trees contain odd number of nodes. So there cannot be full binary trees with 8 or 14 nodes, so rejected. With 13 nodes you can form a complete binary tree but not a full binary tree. So the correct answer is 15.
Note:
Full and Complete binary trees are different. All full binary trees are complete binary trees but not vice versa.
At location 6
1 |
2 |
3 |
- |
- |
4 |
- |
- |
5 |
Root |
LC1 |
RC1 |
LC2 |
RC2 |
LC3 |
RC3 |
LC4 |
RC4 |
where LCn means Left Child of node n and RCn means Right Child of node n
65 |
70 |
75 |
80 |
85 |
60 |
55 |
50 |
45 |
Sorting takes place from the pivot value, which is the first value of the given elements, this is marked bold. The values at the left pointer and right pointer are indicated using L and R respectively.
65 |
70 L |
75 |
80 |
85 |
60 |
55 |
50 |
45 R |
Since pivot is not yet changed the same process is continued after interchanging the values at L and R positions
65 |
45 |
75 L |
80 |
85 |
60 |
55 |
50 R |
70 |
65 |
45 |
50 |
80 L |
85 |
60 |
55 R |
75 |
70 |
65 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
85 L |
60 R |
80 |
75 |
70 |
65 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 R |
85 L |
80 |
75 |
70 |
When the L and R pointers cross each other the pivot value is interchanged with the value at right pointer. If the pivot is changed it means that the pivot has occupied its original position in the sorted order (shown in bold italics) and hence two different arrays are formed, one from start of the original array to the pivot position-1 and the other from pivot position+1 to end.
60 L |
45 |
50 |
55 R |
65 |
85 L |
80 |
75 |
70 R |
55 L |
45 |
50 R |
60 |
65 |
70 R |
80 L |
75 |
85 |
50 L |
45 R |
55 |
60 |
65 |
70 |
80 L |
75 R |
85 |
In the next pass we get the sorted form of the array.
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
65 |
70 |
75 |
80 |
85 |
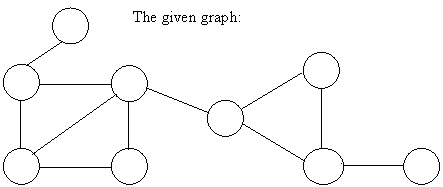
The methods used include:
Overflow block,
The methods used include:
Linked list,
Binary tree…
B+ tree. Because in B+ tree, all the data is stored only in leaf nodes, that makes searching easier. This corresponds to the records that shall be stored in leaf nodes.
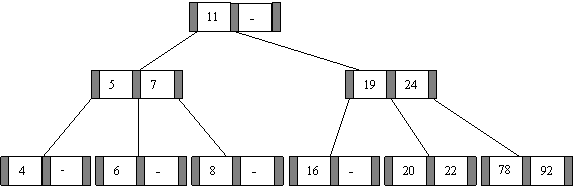
(b) Complete Binary Tree.
By the method of elimination:
Full binary tree loses its nature when operations of insertions and deletions are done. For incomplete binary trees, extra storage is required and overhead of NULL node checking takes place. So complete binary tree is the better one since the property of complete binary tree is maintained even after operations like additions and deletions are done on it.
A spanning tree is a tree associated with a network. All the nodes of the graph appear on the tree once. A minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree organized so that the total edge weight between nodes is minimized.
No.
Minimal spanning tree assures that the total weight of the tree is kept at its minimum. But it doesn’t mean that the distance between any two nodes involved in the minimum-spanning tree is minimum.
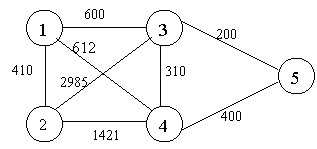
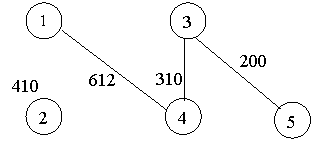
![]() the equivalent minimal spanning tree is:
the equivalent minimal spanning tree is:
(a) Sequential
According to Access strategies Linked list is a linear one.
According to Storage Linked List is a Non-linear one.
A * B - (C + D) * (P / Q)
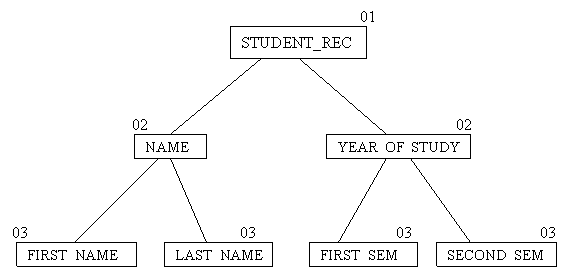
01 STUDENT_REC.
02 NAME.
03 FIRST_NAME PIC X(10).
03 LAST_NAME PIC X(10).
02 YEAR_OF_STUDY.
03 FIRST_SEM PIC XX.
03 SECOND_SEM PIC XX.